
A nonstress test (NST) is a noninvasive test used to monitor an unborn baby’s movement, heart rate, and how its heart rate varies during his or her own movement. If requested by your healthcare provider, the NST is necessary to ensure your baby is healthy and getting enough oxygen. There is no need for you to stress about this test – it’s quick, painless, requires no preparation, and gets its name because it puts no stress on you or the baby!
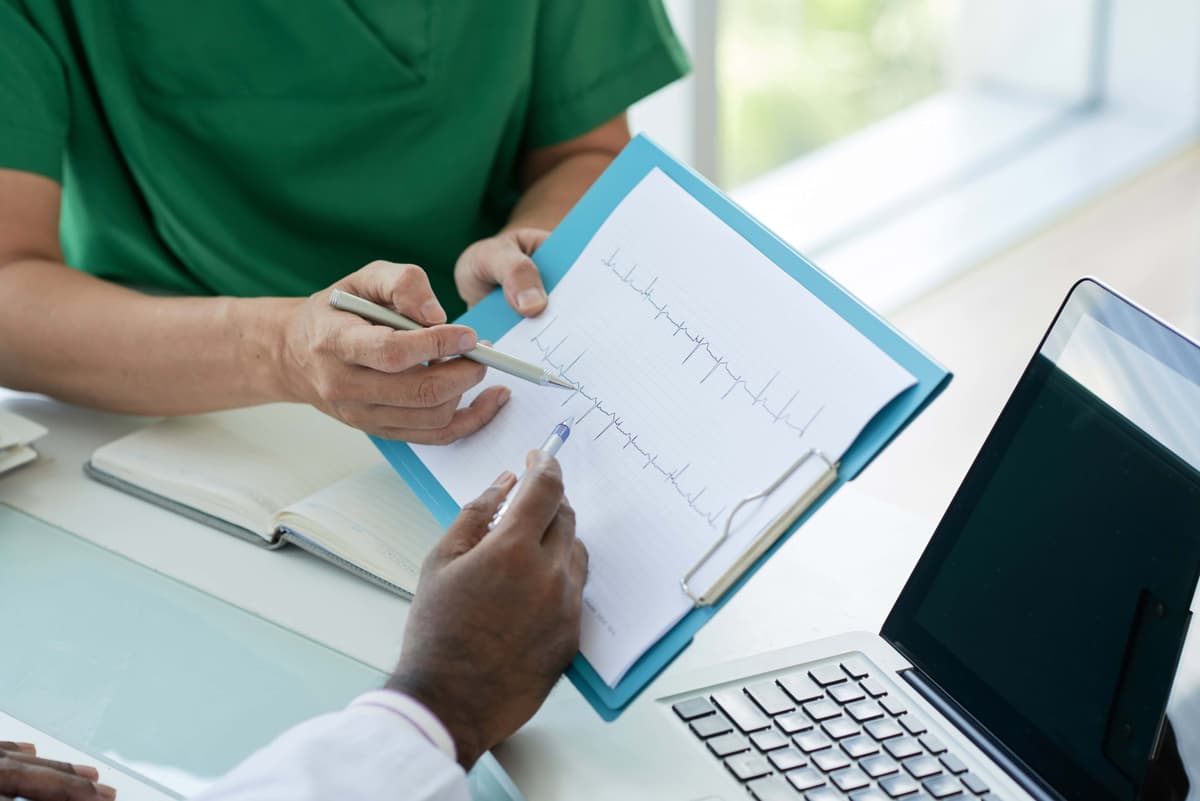

A nonstress test monitors an unborn baby’s movement and heart rate during pregnancy. It typically takes 20 to 30 minutes to measure the fetus’s heart rate and see if it changes as movement occurs. The NST is common, but isn’t required during every pregnancy, as it’s typically recommended when it’s believed that a baby is at an increased risk for complications. If the fetus’s heart rate doesn’t react to movement, your healthcare provider will recommend any future testing or special care that might be necessary.
An NST is requested when a healthcare provider wants to check on the health of the fetus. Your healthcare provider might recommend an NST if:
If needed, NSTs are usually performed after 28 weeks of pregnancy, as this is typically the time when a baby’s heart rate will start reacting to movements. Your healthcare provider may recommend having nonstress tests as often as every day, depending on your health and your baby’s health.
During your NST, you’ll start by lying down on your left side. Your healthcare provider will attach two monitors to you, one to track the baby’s heartbeat and movement, and the other to record contractions. This will continue for 20 to 30 minutes. If the baby isn’t moving, the technician may try various techniques to stimulate them, such as using a buzzer, or asking you to eat or drink. Once the test is finished, the monitors will be removed and you will discuss your results.
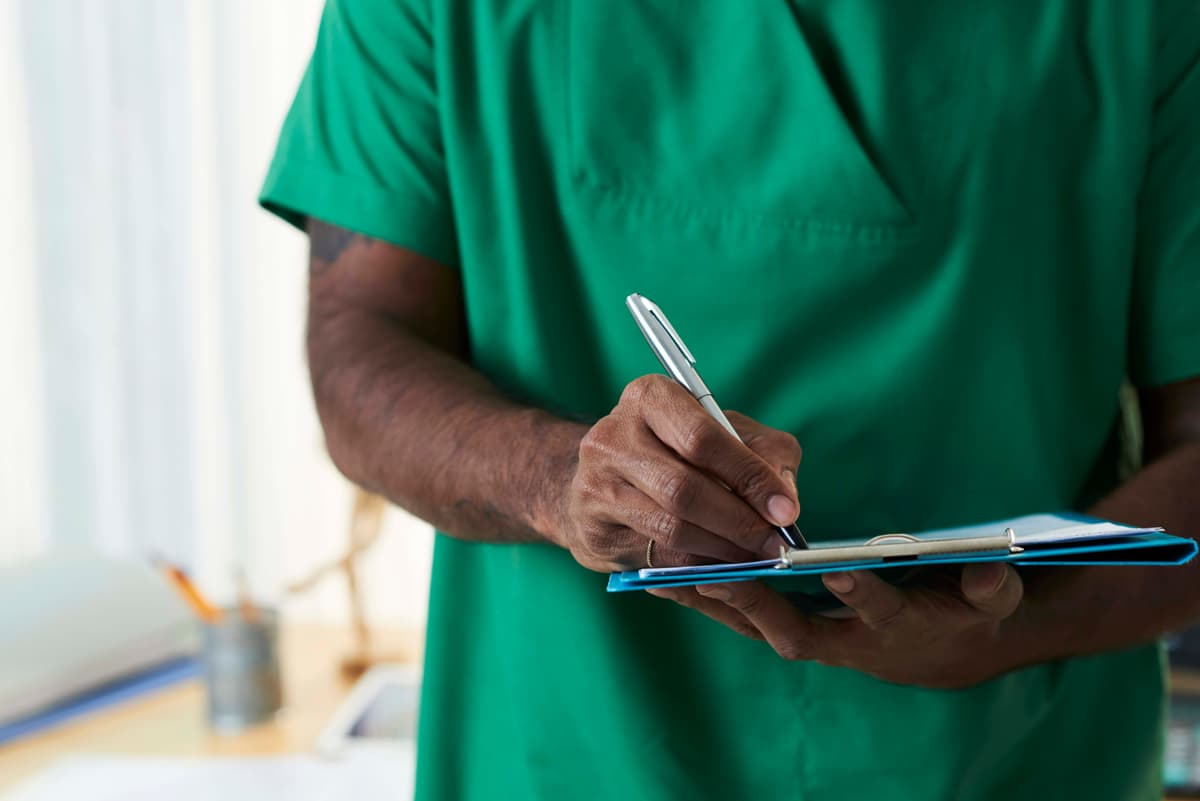

Test results are discussed immediately after the NST. The outcome will either be “reactive” or “nonreactive.” If the NST is “reactive,” it means the fetus’s heart rate increases when he or she moves, or when you have a contraction. This result occurs if the fetus reacts twice within 20 minutes.
If the NST is “nonreactive,” it means the fetus’ heart rate did change as he or she moved. This result doesn’t necessarily mean something is wrong; the fetus could have just been sleeping or not cooperating. The result simply calls for more information, which will likely mean more tests.
Future tests usually include an additional NST, a biophysical profile, which combines an NST with an ultrasound, or a contraction stress test, which measures how the fetus reacts to contractions.
Regardless of the cause or results of your NST, it’s important not to jump to conclusions. The NST is a quick, noninvasive safety measure intended to monitor the health of your baby. You’ll receive the results right away, and any questions you have can be answered by your healthcare provider.

Hot tubs have long been a source of relaxation and social gathering, providing a warm and soothing escape from the stresses of everyday life. However, the relationship between hot tub usage and pregnancy has been a topic of concern and curiosity for many. As expectant parents seek to ensure the health and well-being of their …
Navigating the food landscape for individuals with autism presents formidable challenges. These challenges are compounded by food aversions, sensory sensitivities, and behavioral complexities that can make the simple act of making or ordering food a lot more difficult. Expert research underscores prevalent issues such as tantrums, extreme food selectivity, and nutritional deficiencies among those on …

When catastrophic events such as natural disasters, mass shootings, or acts of violence unfold, children can be left feeling confused, scared, and stressed. Understanding that children respond differently to such situations is crucial. Today, we’ll explore strategies for effectively handling and supporting children as they process these tragedies. Understanding children’s responses to tragedy Children respond …