In today’s interconnected world, our devices are constantly at risk of becoming part of a botnet, a hidden network of compromised computers controlled by cybercriminals. These botnets can operate without the device owner’s knowledge, performing malicious activities such as sending spam, launching attacks, and stealing data. Understanding how botnets work and what threats they pose is crucial for maintaining cybersecurity.

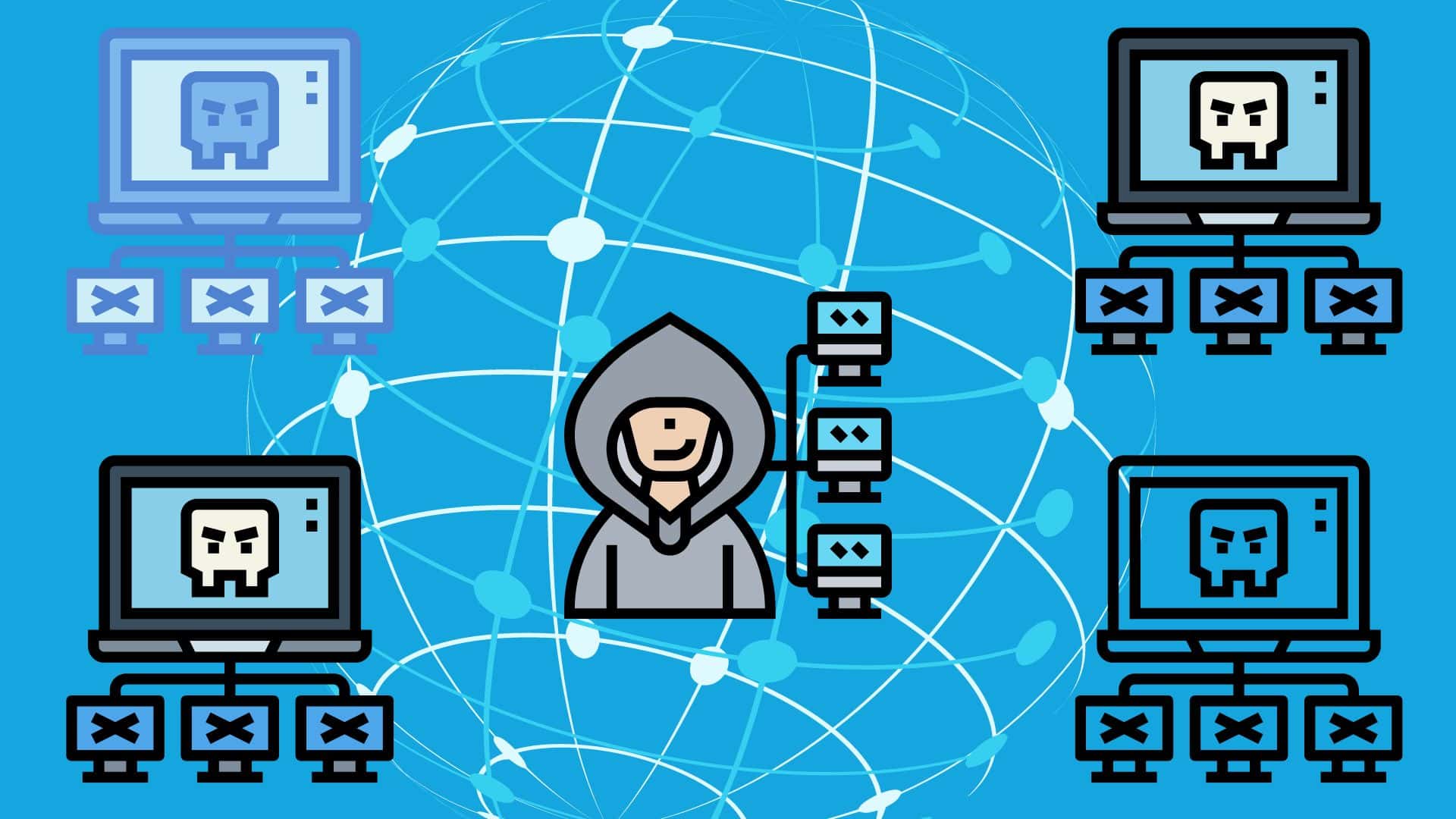
A botnet, derived from the terms “robot” and “network,” is a collection of internet-connected devices, including computers, smartphones, and other smart devices, that have been infected with malware. Once compromised, these devices, known as “zombies,” are controlled by a single operator or a group of cybercriminals, often without the knowledge of the device owners.
The concept of a botnet originates from the idea of using automated software (“bots”) to perform repetitive tasks. When these bots are networked together, they can be used to carry out large-scale activities, often for malicious purposes. The term “botnet” first emerged in the early 2000s as cybercriminals began to realize the potential of coordinating multiple infected devices to conduct sophisticated attacks.

Botnets are versatile tools in the hands of cybercriminals, capable of executing a wide range of malicious activities. One common action is the distribution of spam emails, which can contain phishing links or malware attachments designed to deceive recipients. Botnets also carry out phishing attacks by sending deceptive messages to trick users into revealing sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers.
Another common use of botnets is conducting Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. In these attacks, botnets flood targeted servers with excessive traffic, causing websites or online services to become slow or completely unavailable.
Additionally, botnets can be used for data theft, harvesting personal information such as login credentials and financial details from infected devices. Some botnets use the processing power of infected devices to mine cryptocurrencies, earning money for the operators without the owners’ knowledge. Another common use is ad fraud, where botnets generate fake clicks on online ads to manipulate ad revenue systems.
Detecting botnet infections can be challenging due to their stealthy nature. Botnets often operate silently in the background, making them difficult for users to notice. Common signs of infection include unusual computer behavior, such as slower performance, unexpected crashes, and increased network activity. Users might also experience frequent pop-ups or find unknown programs running on their devices.
Many botnets are sophisticated enough to evade traditional antivirus software. Advanced detection methods involve using specialized malware scanners and monitoring tools that can identify abnormal patterns of activity. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) also play a crucial role in detection, as they can observe unusual traffic patterns and alert users to potential botnet activity.
Updating your system regularly, using robust security software, and practicing safe browsing habits are essential steps in preventing and detecting botnet infections.
Protecting your devices from botnet infections requires a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Start by installing reputable antivirus and anti-malware software and keeping it updated to defend against the latest threats. Regularly update your operating system and applications to patch vulnerabilities.
Practice safe browsing habits by avoiding suspicious links and downloads, and be cautious of phishing attempts. Be sure to use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
Understanding and protecting against botnets is crucial in our increasingly connected world. These hidden networks of compromised devices can perform a range of malicious activities. By implementing strong security practices, regularly updating software, and staying alert to signs of infection, you can significantly reduce the risk of your devices being compromised. Awareness and proactive cybersecurity measures are key to safeguarding your digital life from the hidden dangers of botnets.